WebStorm integrates with the npm, Yarn, Yarn 2, and pnpm, so you can install, locate, update, and remove packages of reusable code from inside the IDE. The Node.js and NPM page provides a dedicated UI for managing packages. Of course, you can also do that from the command line in the built-in Terminal.
WebStorm also lets you run and debug npm, Yarn, and pnpm scripts. WebStorm parses package.json files, recognizing definitions of scripts, shows scripts in a tree view, and lets you navigate between a script in the tree and its definition in the package.json file. See npm, Yarn, and pnpm official web sites for details.
WebStorm detects projects with Yarn workspaces and indexes all the dependencies that are listed in the package.json files of the workspaces but are located in the root node_modules folder.
Before you start
Download and install Node.js. Note that npm is also installed, so if you are going to use it, you are through with the preliminary steps.
To use Yarn, install it as described on the Yarn official website.
To use pnpm, open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type:
npm install --g pnpmLearn more from the pnpm official website.
Choose a project package manager
With WebStorm, you can choose whether to use npm, Yarn, Yarn 2, or pnpm in a project.
By default, WebStorm suggests npm. However if you open a project with a yarn.lock file and Yarn is installed on your computer, WebStorm automatically changes the package manager for this project to Yarn.
WebStorm 2020.2 Beta is now available! To catch up on what has already been implemented in v2020.2, check out our previous EAP blog posts. The Toolbox App is the easiest way to get the EAP builds and keep your stable WebStorm version and any EAP versions up to date. Or you can download the EAP builds from our website.You can also choose to be notified right from the IDE when a new EAP build. That works, but it was an annoyance having to search on Google and find this answer. Strange that it's missing, WebStorm should be able to pick up the package.json and show it as an option in the tool window menu. In previous projects I never used the right-click menu and somehow managed to get the npm scripts window showing.
- Webstorm npm settings. Npm and Yarn, To sort the scripts in a tree by their names. Click Settings on the toolbar, choose Sort by from the menu, and then choose With WebStorm, you can choose whether to use npm, Yarn, or Yarn 2 in a project. By default, WebStorm suggests npm.
- That's the output of volta which npm, but in the linked WebStorm issue, you said that Volta is pointing to npm-cli.js, which is a sibling file to the npm shell script, but I.
Accordingly, if you open a project with a pnpm-lock file and pnpm is installed on your computer, WebStorm automatically changes the package manager for this project to pnpm.
You can also set Yarn 1 or pnpm as default WebStorm package manager.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to Languages and Frameworks | Node.js and NPM. The Node.js and NPM page opens.
In the Package manager field, specify the package manager for your project.
Select npm, yarn, or pnpm to use the system default installation.
WebStorm uses the
npm,yarn, andpnpmaliases for the current system paths to these managers. If you choose another Node.js version, WebStorm also changes the npm aliased path to point to the npm version bundled with the selected Node.js version.To use a custom installation of a package manager, click Select, and select the installation folder of the relevant package manager.
WebStorm automatically uses the chosen package manager when you select the
Projectalias from the Package manager list in the Run/Debug Configuration: NPM dialog. WebStorm also uses the path to the chosen package manager every time you invoke the Run 'npm install'/ Run 'yarn install'/ Run 'pnpm install' command or run an npm/Yarn/pnpm script, see Running and debugging scripts for details.
Set up Yarn 2 in your project
Make sure you have Yarn 1 installed globally and enable Yarn 2 in your project as described on the Yarn official website. Use the embedded TerminalAlt+F12 to type the commands.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to Languages and Frameworks | Node.js and NPM and select the path to the Yarn 2 package in your project from the Package manager list.
Set Yarn 1 or pnpm as the default WebStorm package manager
Open the Settings for New Projects dialog (File | New Projects Settings | Settings for New Projects) and go to Languages and Frameworks | Node.js and NPM.
On the Node.js and NPM page that opens, select
yarnorpnpmfrom the Package manager list.
Webstorm Npm Free
After that, WebStorm will suggest the selected package manager (Yarn or pnpm) as default every time you create a new project.
Edit package.json
WebStorm helps you handle your project dependencies in package.json files providing extensive coding assistance.
Code completion for package names.
Information on the latest available package version.
Information about the range of versions that can be installed through
npm install <package>@<version>oryarn add <package>@<version>. `Note that runningnpm installoryarn installwill install the latest available version from this range.Press Ctrl and hover over the version to see the information in a tooltip. See the npm Official documentation for details about semantic versioning.
Code completion for previous package versions. When you press Ctrl+Space or start typing a version different from the latest one, WebStorm displays a suggestion list with all the previous versions of the package.
Quick documentation look-up for packages.
WebStorm also shows readme files for npm packages when you invoke documentation look-up from
requireorimportstatements.
Install and update packages
As you may know, npm can install packages both globally or as project dependencies or development dependencies, learn more from the npm official website.
pnpm also installs packages globally or as project dependencies or development dependencies, learn more from the pnpm official website.
With Yarn, you can install packages globally or as project dependencies, see Yarn official website for details.
In WebStorm, packages can be installed in the editor, from a package.json file, in the built-in TerminalAlt+F12, or on the Node.js and npm page.
From package.json
Install your project dependencies
Click the Run 'npm install', Run 'yarn install', or Run 'pnpm install' link in the popup:
WebStorm shows this popup when the dependencies are not installed yet or when they have changed. If you close the popup or turn it off by choosing Don't ask again, you can still install the dependencies using the Run '<package_manager> install' action or in the built-in terminal.
If you have accidentally dismissed this notification and now want to get it back, press Ctrl+Shift+A, start typing
Enable notifications, and select Enable Notifications about Installing Dependencies from package.json from the list.Alternatively, open the relevant package.json file in the editor or select it in the Project tool window and choose Run 'npm install' from the context menu.
Update your project dependencies
Click Run '<package manager> install' in the popup.
WebStorm shows this popup every time you open a project, update it from the version control, or edit a package.json.
WebStorm also runs an inspection that checks whether the packages from
dependenciesordevDependenciesare installed and their versions match the specified range. If the inspection detects any mismatch, it suggests a quick-fix. To apply it, click the Run '<package manager> install' link.
In the built-in Terminal
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12), type one of the following commands:
For global installation:
npm install --global <package_name>yarn global add <package_name>pnpm --global add <package_name>
To install a package as a project dependency or a development dependency:
npm install --save <package_name>ornpm install --save-dev <package_name>yarn add <package_name> --devpnpm add --save-dev <package_name>
Install all dependencies listed in a package.json file
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12), type one of the following commands:
npm installyarn installpnpm install
As a result you get all the dependencies listed in the package.json from the current folder. Learn more from Editing package.json.
For packages installed via Yarn 2, WebStorm shows yarn:package.json:< package name> instead of the actual path to a package. Note that this format is used only for presenting a package in the Settings dialog but not for specifying its location in your code or elsewhere.
On the Node.js and NPM page
WebStorm shows all the currently installed packages on the Node.js and NPM page. To open the page, in the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to Languages and Frameworks | Node.js and NPM.
Globally installed packages are listed on top. For each package, WebStorm shows its currently installed version and the latest available version.
Install a package
Click and in the Available Packages dialog that opens, select the required package.
By default, the latest package version is installed. To install another one, select the Specify version checkbox and choose the required version from the list.
The default installation is local. To use another installation type, select the Options checkbox and type
-gfor global installation or--save/--save-devto install the package as a dependency/development dependency. Learn more from the npm and Yarn official websites.
View the location of a package
Hover the mouse pointer over the package name. WebStorm shows the path to the package in a tooltip.
Update a package to the latest version
Select the package in the list and click .
Remove a package
Select the package in the list and click .
Run and debug scripts
You can launch npm, Yarn, or pnpm scripts from a package.json file in the editor, from a tree of scripts in the dedicated npm tool window, according to a dedicated run configuration, or automatically, as a start-up or a before-launch task.
The results of script execution are displayed in the Run tool window. The tool window shows the npm or Yarn script output, reports the errors occurred, lists the packages or plugins that have not been found, etc. The name of the last executed script is displayed on the title bar of the tool window.
If you launch a script debugging session, WebStorm opens the Debug tool window.
During a script debugging session, you can step through the script, stop and resume the script execution, examine it when suspended, run JavaScript code snippets in the Debugger Console, and so on.

Run and debug scripts from package.json
WebStorm lets you quickly launch single scripts from package.json files. To run or debug several scripts, use a run configuration or the npm tool window.
Open the package.json file in the editor, click in the gutter next to the script, and choose Run <script_name> or Debug <script_name> from the context menu.
You can also run a script by pressing Ctrl+Shift+F10.
The script output is shown in the Run tool window.
If you launch a script in the debug mode, WebStorm opens the Debug tool window, where you can step through the script, stop and resume the script execution, examine it when suspended, run JavaScript code snippets in the Debugger Console, and so on.
Run and debug scripts from the npm tool window
The tool window opens when you select a package.json file in the Project tool window or open it in the editor and choose Show npm Scripts from the context menu. As soon as you invoke npm or Yarn, it starts building a tree of scripts defined within the scripts property of the package.json file on which it was invoked. If you have several package.json files in your project, you can build a separate script tree for each of them and run scripts without dropping the previously built trees. Each tree is shown under a separate node.
Open the npm tool window if it is not opened yet
Select the required %fileName% file in the Project tool window or open it in the editor and choose Show npm Scripts from the context menu.
The npm tool window opens showing the scripts tree built according to the selected or opened package.json file.
Build a tree of scripts in an already opened npm tool window
In the npm tool window, click on the toolbar and choose the required package.json file from the list. By default, WebStorm shows the package.json file in the root of your project.
If you have another package.json file, click Choose package.json and select the package.json file you need in the dialog that opens. WebStorm adds a new node with the path to the chosen package.json file on its title and builds a scripts tree under the new node.
Re-build a tree
Switch to the required node and click on the toolbar.
Sort the scripts in a tree by their names
Click on the toolbar, choose Sort by from the menu, and then choose Name.
By default, a tree shows the scripts in the order in which they are defined in package.json (option Definition order ).
Webstorm Npm
Run one script
Double-click the script.
Select the script in the tree and press Enter or choose Run <script name> from the context menu.
Debug one script
Select the script in the tree and choose Debug <script_name> from the context menu.
WebStorm opens the Debug tool window where you can step through the script, stop and resume the script execution, examine it when suspended, run JavaScript code snippets in the Debugger Console, and so on.
Run or debug several scripts
Use the multiselect mode: hold Shift (for adjacent items) or Ctrl (for non-adjacent items) keys and select the required scripts, then choose Run or Debug from the context menu of the selection.
Run and debug scripts by a run configuration
When you run or debug scripts from the editor or from the npm tool window, WebStorm automatically creates temporary run configurations. Besides using them, you can create and launch your own npm run configurations.
From the main menu, select Run | Edit Configuration.
Click on the toolbar and select npm from the list. The Run/Debug Configuration: npm dialog opens.
Specify the CLI command to execute, the scripts to run (use blank spaces as separators), and the location of the package.json file where these scripts are defined. Optionally, type the command-line arguments for executing the scripts.
- Specify the Node.js interpreter to use. This can be a local Node.js interpreter or a Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Optionally, specify the Node.js-specific option parameters and the environment variables to be passed to Node.js.
Specify the package manager to use. If you choose the
Projectalias, WebStorm will use the default project package manager from the Node.js page. You can also choose the relevant package alias (npm or yarn) or specify an explicit path to a custom installation of a package manager.Select the newly created run configuration from the list on the toolbar and then click or next to the list.
The results of script execution are displayed in the Run tool window.
If you click , WebStorm opens the Debug tool window, where you can step through the script, stop and resume the script execution, examine it when suspended, run JavaScript code snippets in the Debugger Console, and so on.
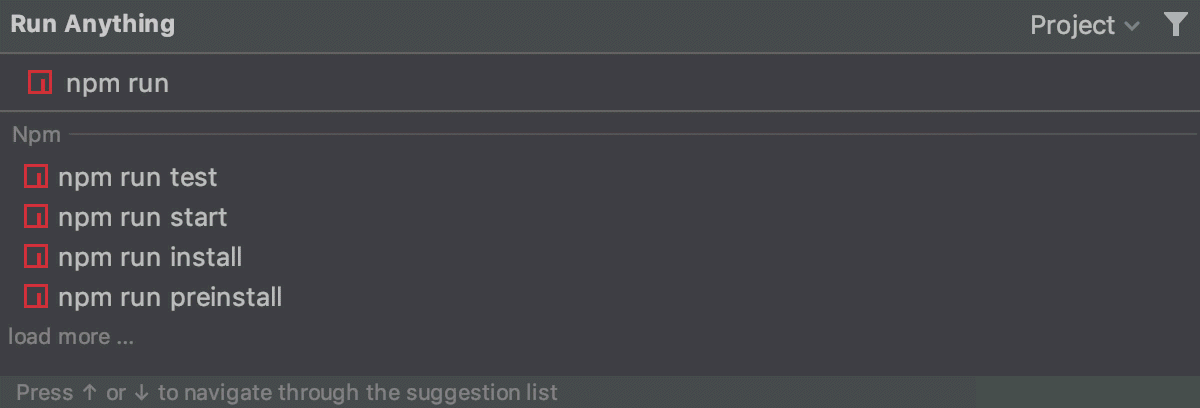
Run scripts with Run Anything
Run Anything is a quick way to start scripts.
Press Ctrl twice or click on the Navigation bar. The Run Anything popup opens.
Type
npm runoryarn runin the search field. As you type, WebStorm shows the matching scripts. Select the required one from the list and press Enter.To view the command output in the Run tool window, press Ctrl+Enter, to show the output in the Debug tool window, press Shift+Enter.
Run Anything is also a quick way to launch applications and to reopen recent projects, learn more from Running applications and Opening, reopening, and closing projects.

To see all available commands, type ?.
Run scripts automatically on start-up
If you have some scripts that you run on a regular basis, you can add the corresponding run configurations to a list of startup tasks. The tasks will be executed automatically on the project start-up.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to Tools | Startup Tasks.
On the Startup Tasks page that opens, click on the toolbar.
From the list, choose the required npm run configuration. The configuration is added to the list.
If no applicable configuration is available in the project, click and choose Edit Configurations. Then define a configuration with the required settings on the Run/Debug Configuration: NPM page that opens. When you save the new configuration it is automatically added to the list of startup tasks.
Run scripts as before-launch tasks
Open the Run/debug configurations dialog dialog by choosing Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu, and select the required configuration from the list or create it anew by clicking and choosing the relevant run configuration type.
In the dialog that opens, click in the Before launch area and choose Run npm script from the list.
In the NPM Script dialog that opens, specify the npm run/debug configuration settings.
This tutorial describes how to use the Karma test runner in the WebStorm IDE.
- Running tests
Karma integration in WebStorm
Starting with WebStorm 7.0, you can use the Karma test runner to run JavaScript tests for your project.
Karma integration in WebStorm:
- Uses local server to run the tests in the selected browsers installed on your computer;
- Allows you to run tests written with the use of Jasmine, QUnit, or Mocha, or to write a simple adapter to use any other framework you like;
- Presents test results and code coverage report by the istanbul code coverage engine right in the IDE.
Installing Karma
First, make sure that Node.js is installed on your computer.
Install Karma usingnpm:
The recommended approach is to install Karma (and all the plugins your project needs) locally in the project's directory.
Use WebStorm’ built-in npm ( Settings | JavaScript | Node.js and NPM) search and install Karma for your project.
Or install it in the current directory using Terminal:
Installkarma-cliglobally:
Use WebStorm’ built-in npm and search for karma-cli, add -g option before hitting Install for global installation.
Or use built-in Terminal to install karma-cli with:
Karma configuration
To run new tests with Karma, you need to have a Karma configuration file (learn more about it).
To generate new configuration file, for example, karma.conf.js in the project directory run in built-in Terminal:
Follow the suggested steps in the configuration dialog.

Note: Most of the framework adapters, reporters, preprocessors and launchers need to be loaded as plugins.
Create a WebStorm Karma Run Configuration:
- Click Create 'karma.conf.js' in the context menu for karma.conf.js file
- Check the paths in the Create Run/Debug Configuration window
- Click OK.
Running tests
Run
A new Karma Configuration will be added to the list of Run/Debug Configurations.
To start running your tests, click Run in the toolbar or in the context menu of Karma configuration file.
Note: WebStorm disables autoWatch in Karma configuration.
You can rerun your tests with the shortcut Alt+Shift+R on Win/Linux or ctrl-cmd-R on Mac.
Click auto-test in the WebStorm Test Run window to enable automatic test rerun: The test will be run 10 seconds after your code was changed, if there are no syntax errors.
Run with coverage
WebStorm Karma integration allows you to run tests with code coverage provided by the istanbul code coverage engine.
To use Run with coverage feature, a karma-coverage module should be installed via npm.
Make the required changes in the Karma configuration file, for example:
You can navigate through test results in the Run window, check statistics for the tests execution, and make HTML reports from it. Code coverage report will be also available.
